Urenco USA plays a key role in the nuclear fuel supply chain, enabling the generation of reliable, low-carbon electricity for consumers worldwide.
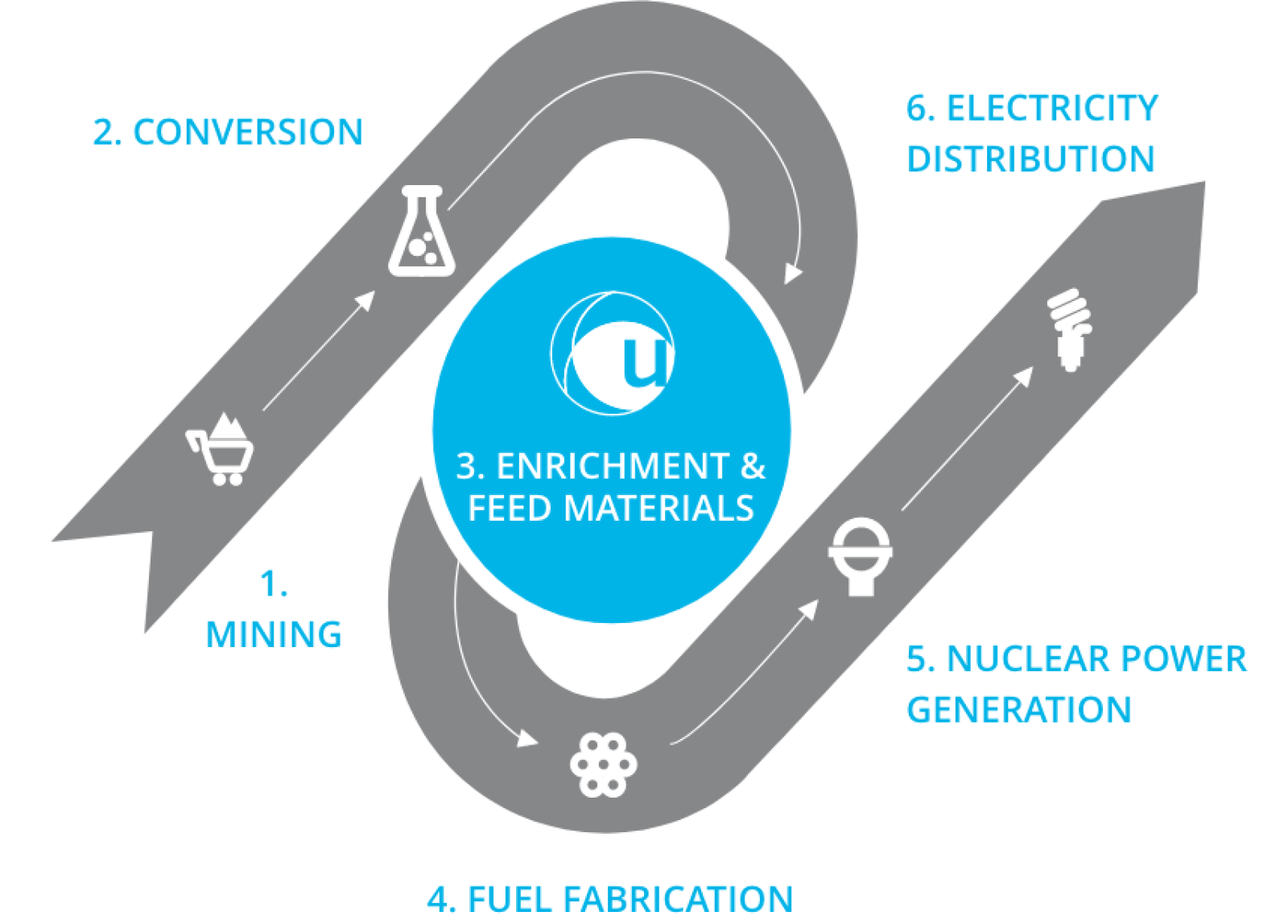

1. Mining
Uranium ore is extracted, purified and milled to become uranium oxide (U3O8).
2. Conversion
U3O8 is chemically converted into uranium hexafluoride (UF6), also known as feed, and transported to our facility.
3. Enrichment
Our enrichment process starts with the arrival of our customers’ UF6 at our facility. We heat UF6 to turn it into a gas and feed it into our gas centrifuges.
The centrifuge separates the two isotopes contained in uranium: uranium235 (U235) and uranium238 (U238). The lighter U235 is typically enriched to up to 5%, which is sufficient to sustain a continuous fission reaction in a nuclear power plant.
The flexibility of our centrifuges allows us to conserve feed material and therefore provide enriched uranium product and natural uranium in addition to enrichment services.
4. Fuel Fabrication
The customers’ enriched uranium is transported to fuel fabricators, where it is converted into pellets before being loaded into fuel rods.
5. Nuclear Power Generation
The fuel rods are transported to nuclear power stations, where they are placed into reactors and used to generate steam. This drives turbines which in turn power electricity generators.
6. Electricity Distribution
At the end of the nuclear fuel supply chain, nuclear power stations provide a reliable source of low carbon electricity for homes, schools, hospitals, offices and industries around the world.





